We often associate the rise of greenhouse gases with climate change. But exactly how do greenhouse gases affect our atmosphere?
Basically, greenhouse gases are gases in the earth’s atmosphere that trap heat.
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases are the four major greenhouse emissions.
To understand the greenhouse gases, we have to talk about the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse effect
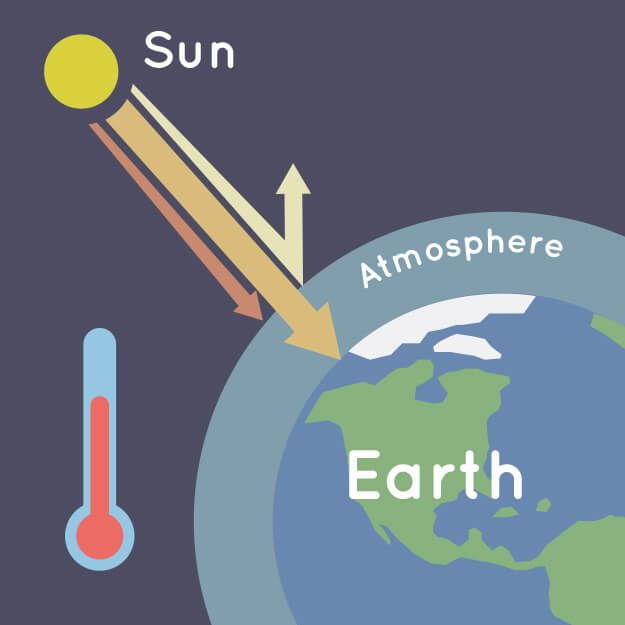
The greenhouse effect is a process when gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap the sun’s heat. The process is similar in how a greenhouse works to grow plants.
Earth’s atmosphere traps some of the Sun’s heat, preventing it from escaping back into space at night. (NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Gases in the atmosphere trap heat just like the roof of a greenhouse. The greenhouse effect is also balanced by our plants and oceans absorbing carbon dioxide.
However, too much greenhouse gases increase the warming of our planet, which leads to climate change.
So let’s talk about each greenhouse gas and how it affects our atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide is the biggest contributor to climate change. CO2 is a compound that occurs in the Earth’s atmosphere and is also produced by human activities. It accounts for 79% of U.S. greenhouse gases.
The chemical is usually emitted through burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas) and being extracted from other biological material.
Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere when it is absorbed by plants through a process called the carbon cycle.
Methane (CH4)
Methane is the key component of natural gas and makes up 12% of U.S. greenhouse emissions. The chemical is emitted through mining coal and using natural gas.
It is also released from wetlands, raising livestock and other agricultural activities.
Methane traps a lot of heat. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says methane traps 25 times more heat than carbon dioxide.
Nitrous oxide (N2O)
Nitrous oxide makes up 6% of the U.S. greenhouse emissions. The compound is present in the atmosphere through the nitrogen cycle.
Bacteria in the ocean and soil make N2O. The gas is also released through factories, fuel combustion, power plants and plant feritilizers.
Nitrous oxide traps more heat than carbon dioxide. The EPA says “the impact of 1 pound of nitrous oxide on warming the atmosphere is 265 times that of 1 pound of carbon dioxide.”
The chemical depletes our ozone layer and exposes the Earth to more sun radiation.
Fluorinated gases (chlorofluorocarbons)
Fluorinated gases or Chlorofluorocarbon (CFCs) make up 3% of U.S. greenhouse emissions. These gases are manmade.
These chemicals deplete our ozone layer.
There are four types of CFCs: hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3).
We emit CFCs in multiple ways. These range from manufacturing to aerosols to refrigerants and products containing ozone-depleting substance.
Our team of meteorologists dives deep into the science of weather and breaks down timely weather data and information. To view more weather and climate stories, check out our weather blogs section.